Guyana - Introduction
Guyana (officially: Co-operative Republic of Guyana) is a country in Americas, precisely in South America, with a population of about 823.9 Thousands inhabitants today (2025-04-19). The capital city of Co-operative Republic of Guyana is Georgetown, and the official country TLD code is .gy. Guyana has cca2, cca3, cioc, ccn3 codes as GY, GUY, GUY, 328 respectively. Check some other vital information below.

Guyana , Coat of Arms
Names
| Common | Guyana |
|---|---|
| Official | Co-operative Republic of Guyana |
| Common (Native) | Guyana |
| Official (Native) | Co-operative Republic of Guyana |
| Alternative spellings | GY, Co-operative Republic of Guyana |
| Translations ⬇️ | |
Languages
| eng | English |
|---|
Geography
Guyana is located in South America and has a total land area of 214969 km². It is bounded by Brazil, Suriname, Venezuela and the capital city is Georgetown
| Region/Continent | South America |
|---|---|
| Subregion | South America |
| TimeZone | UTC-04:00 |
| Capital city | Georgetown |
| Area | 214969 km² |
| Population 2025-04-19 | 823.9 Thousands |
| Bordered Countreies | Brazil, Suriname, Venezuela |
| Demonym | |
| eng | Male: Guyanese / Female: Guyanese |
| fra | Male: Guyanien / Female: Guyanienne |
| Lat/Lng | 5, -59 |
Historical data and more

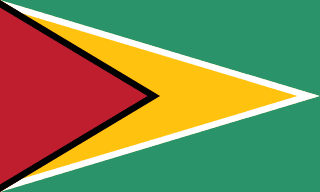
The National Flag of Guyana
The flag of Guyana has a green field with two isosceles triangles which share a common base on the hoist end. The smaller black-edged red triangle spanning half the width of the field is superimposed on the larger white-edged yellow triangle which spans the full width of the field.
| Currency | |
|---|---|
| Name | Guyanese dollar |
| Code | GYD |
| Symbol | $ |
| Other info | |
| Idependent | yes, officially-assigned |
| UN Member country | yes |
| Start of Week | monday |
| Car Side | left |
| Codes | |
| ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 | GY |
| ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 | GUY |
| ISO 3166-1 numeric | 328 |
| International calling code | +592 |
| FIFA 3 Letter Code | GUY |
All Important Facts about Guyana
Want to know more about Guyana? Check all different factbooks for Guyana below.

